Introduction
Regarding baking, cake, and bread are two staples that bring joy to many. They both have unique characteristics that make them delicious in their ways. Understanding the difference between cake and bread is important for bakers and baking enthusiasts. This article will delve into the key factors that set cake and bread apart, from their ingredients to their textures and intended uses. By the end of this article, you’ll better grasp the baking basics and be able to differentiate between these two beloved treats.
Understanding The Difference Between Cake And Bread
While cake and bread share some similarities, their differences outweigh their likeness. Here are the key factors that distinguish cake from bread:
- Ingredients: The main difference between cake and bread is their ingredients, especially the leavening agents. Bread is traditionally leavened with yeast, while cake is leavened with baking powder or baking soda. Additionally, sugar, eggs, milk, and fat are more prevalent in cake recipes, giving them a sweeter and richer flavor than bread.
- Texture: Texture plays a significant role in differentiating cake from bread. Bread has a denser and chewier texture due to the gluten formation in the dough. Conversely, the cake is lighter and more tender with a soft and moist crumb. The use of different ingredients and leavening agents contributes to these contrasting textures.
- Intended Use: Bread is commonly regarded as a staple food consumed regularly. Its main purpose is to provide sustenance. On the other hand, cake is often associated with special occasions and celebrations. It is meant to be indulgent and enjoyed as a treat.
- Nutritional Content: The overall nutritional content of cake and bread differs significantly. Bread is generally considered healthier as it is typically made with whole grains and contains more fiber and essential nutrients. Cake, being sweeter and more decadent, tends to have higher sugar and fat levels.
- Leavening Agent: The leavening agent used in bread, typically yeast, allows it to rise slowly over time. In contrast, cake recipes rely on quick-acting leavening agents like baking powder or baking soda, rapidly producing carbon dioxide bubbles, resulting in a lighter texture.
- Flavor Profile: Bread has a more neutral flavor profile, allowing it to complement a variety of toppings or fillings. On the other hand, cake comes in a wide range of flavors, often enhanced by additional ingredients like fruits, nuts, or extracts.
- Baking Techniques: Baking techniques for cake and bread also differ. Bread is often kneaded and requires longer rising times, while cakes are typically mixed and baked in less time.
In conclusion, while cake and bread may seem similar initially, their distinct characteristics set them apart. Understanding the differences in ingredients, texture, intended use, and baking techniques is essential for achieving the desired results in baking. So whether you’re craving a slice of bread or a cake, you now understand what makes these baked goods unique.
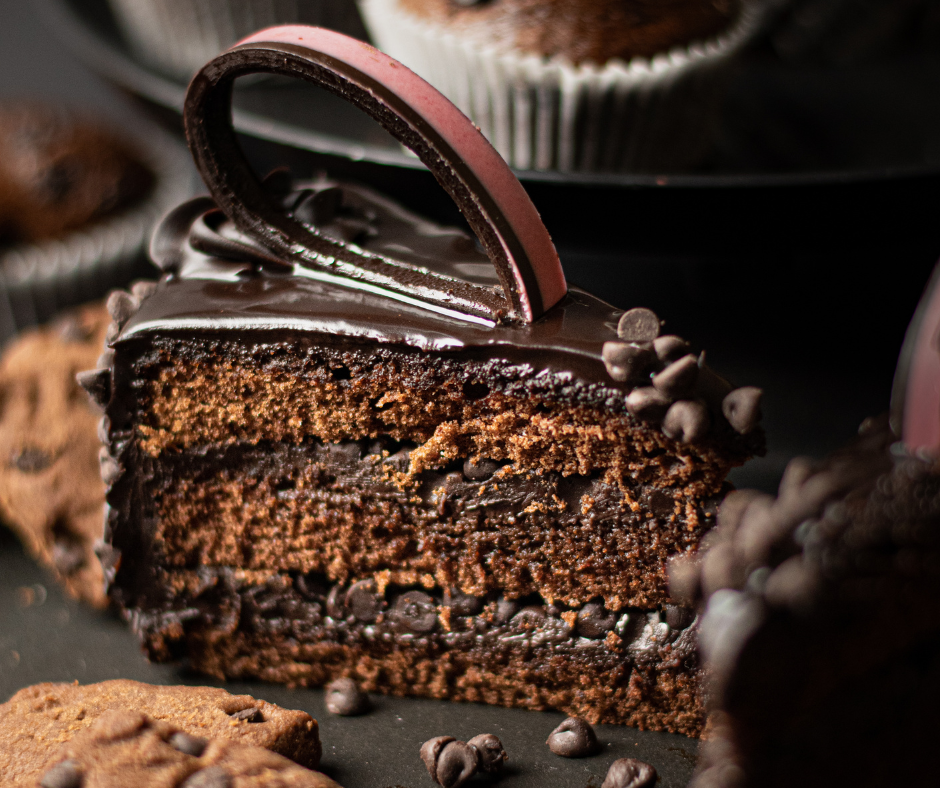
Cake Basics
Ingredients Used In Cakes
When it comes to baking cakes, a few key ingredients are essential in creating the perfect treat. These ingredients include flour, sugar, eggs, fat (usually butter or oil), liquid (such as milk or water), salt, and leavening agents. Combining these ingredients determines your cake’s flavor, texture, and overall success.
Flour provides structure to the cake, giving it a soft and tender crumb. Sugar sweetens the cake, adds moisture, and helps with browning. Eggs are crucial in cakes, acting as a binding agent and adding richness. Whether butter or oil, fat contributes to the cake’s texture and moistness, and liquid, such as milk or water, helps to hydrate the ingredients and create a smooth batter. Salt enhances the flavor of the cake, balancing the sweetness. Lastly, leavening agents like baking powder and baking soda create air bubbles, causing the cake to rise and become light and fluffy.
Leavening Agents In Cakes: Baking Powder And Soda
Leavening agents are essential for achieving a light and airy texture in cake baking. The primary leavening agents used in cakes are baking powder and baking soda. While these two ingredients have similar functions, they react differently in the batter.
Baking powder combines baking soda, an acid (such as cream of tartar), and a stabilizer (usually cornstarch). When the baking powder is mixed with liquid and heat is applied during baking, the acid and baking soda react, creating carbon dioxide bubbles that expand the batter. This reaction results in the cake rising and becoming fluffy.
Baking soda, on the other hand, is a single-ingredient leavening agent. It requires the presence of an acid (such as buttermilk, yogurt, or vinegar) to create the necessary chemical reaction for the cake to rise. Carbon dioxide is released as the acid and baking soda combine, causing the batter to expand and the cake to rise.
Understanding the proper usage of these leavening agents is crucial for achieving the desired texture in your cake. Too much or too little can result in a dense or flat cake, while the right balance can create a perfectly light and airy treat.
By understanding the basic ingredients used in cakes and the role of leavening agents like baking powder and baking soda, you can master the art of cake baking. So the next time you’re in the kitchen, armed with these baking basics, you can create delicious and impressive cakes that will delight your taste buds. Happy baking!
Bread Basics
Ingredients Used In Bread
When it comes to baking bread, there are a few key ingredients that are necessary for success. These ingredients include flour, water, salt, and yeast. Each ingredient plays a specific role in creating the perfect loaf of bread.
Flour is the foundation of bread, providing structure and texture. Water is essential for hydrating the dough and activating the yeast. Salt enhances the bread’s flavor and helps control the fermentation process. And lastly, yeast is the primary leavening agent in bread, responsible for the rising and fermentation process.
Leavening Agent In Bread: Yeast
Yeast is a microorganism that plays a crucial role in bread baking. It is responsible for fermentation, which consumes sugars in the dough and produces carbon dioxide gas. This gas gets trapped in the dough, causing it to rise and create air pockets, resulting in a light and fluffy texture.
Different types of yeast are available, such as active dry yeast, instant yeast, and fresh yeast. Each type has its characteristics and requirements for activation. Active dry and instant yeast are the most commonly used types in bread baking. Active dry yeast must be dissolved in warm water before adding it to the dough, while instant yeast can be added directly to the dry ingredients.
To successfully use yeast in bread baking, it is important to activate it properly. This can be done by dissolving the yeast in warm water with a small amount of sugar and allowing it to sit for a few minutes until it becomes foamy. This indicates that the yeast is active and ready to be added to the dough.
Understanding the role of yeast and the other essential ingredients in bread baking is crucial for achieving the perfect loaf. By mastering the art of bread-making, you can enjoy the satisfaction of creating delicious homemade bread that will impress your family and friends.
So, armed with this knowledge of the ingredients and leavening agent in bread, embrace the world of bread baking. From crusty artisan loaves to soft sandwich bread, the possibilities are endless. Happy baking!

Difference Between Cake and Bread: Texture And Consistency
Texture Of Cakes
Cakes are known for their wide range of textures, from dense and moist to light and airy. The texture of a cake depends on various factors, such as the ingredients used, mixing method, and baking time. Cakes with a tight crumb, baked in a regular round or square cake pan, often make nice bread-shaped slices when baked in loaf pans. This is why some cakes baked in loaf pans are sometimes called bread, like banana or pumpkin bread.
When mixing cake batter, recipes often instruct to mix until just incorporated. This is done to ensure that the batter is evenly mixed without over-mixing, which would result in gluten formation. Unlike bread, cakes generally do not want gluten formation, so they use flour with a lower gluten content, such as all-purpose flour or cake flour. This results in a more tender and delicate texture.
Texture Of Bread
Bread has a distinct texture that is chewy and bready. The texture of bread is achieved through a different approach compared to cakes. Bread recipes use flour with a higher gluten content, such as bread or whole wheat flour. These flours contain more protein, which creates stronger gluten strands when mixed and kneaded.
The mixing and kneading process in bread-making aligns these gluten strands and gives the bread its characteristic structure. This structure traps carbon dioxide produced by yeast during fermentation, resulting in the bread rising and creating air pockets. This gives bread its chewy and slightly elastic texture.
In addition to gluten formation, bread requires a longer fermentation process than cakes. The yeast in bread consumes sugars in the dough and produces carbon dioxide gas, contributing to the bread’s rise and texture. This longer fermentation allows for a deeper flavor development in the bread.
Understanding the Difference Between Cake and Bread in texture and consistency is essential for successful baking. Whether you prefer the tender and moist texture of cakes or the chewy and bready texture of bread, experimenting with various recipes and techniques will allow you to create delicious baked goods that satisfy your cravings.
By knowing the basics of cake and bread baking, you can confidently explore the world of baking and create mouthwatering treats to delight yourself and others. So, roll up your sleeves, preheat the oven, and prepare for your baking adventures!
Baking Methods And Techniques
Understanding the Difference Between Cake and Bread is essential for any aspiring baker. While they may share some similarities, the baking process for each is distinct. Here, we will explore the baking methods and techniques for cake and bread, giving you a better understanding of the basics.
Cake Baking Process
Baking a cake involves a delicate balance of ingredients and techniques to achieve the desired texture and consistency. Here are the key steps in the cake-baking process:
- Preparation: Preheat the oven and prepare the cake pans by greasing and flouring them to prevent sticking.
- Mixing: In a separate bowl, combine the dry ingredients such as flour, baking powder, and salt. In another bowl, cream the butter and sugar until light and fluffy. Then, add eggs and other wet ingredients, alternating with the dry ingredients, mixing until just incorporated.
- Baking: Pour the batter into the prepared cake pans and bake in the oven for the specified time. The cake is done when a toothpick inserted into the center comes clean.
- Cooling and Frosting: Allow the cakes to cool completely before removing from the pans. Once cooled, you can frost and decorate the cakes according to your preference.
Bread Baking Process
Bread baking is a more involved process that relies on yeast fermentation to create gluten structures and produce the desired texture. Here are the key steps in the bread-baking process:
- Activation: Activate the yeast by proofing it in warm water or milk with a small amount of sugar. This step ensures that the yeast is active and will ferment the dough.
- Mixing and Kneading: In a mixing bowl, combine the flour, yeast mixture, and other ingredients. Knead the dough by hand or using a stand mixer until it becomes smooth and elastic. The kneading process develops the gluten strands that give bread its structure.
- First Proof: Place the dough in a greased bowl, cover it with a clean towel, and let it rise warmly for the first proofing. This allows the yeast to ferment the dough and create carbon dioxide gas, causing the dough to rise.
- Shaping and Second Proof: Punch down the dough to release excess gas after the first proof. Shape the dough into the desired form, whether a loaf, roll, or other shapes. Allow the shaped dough to rest and rise again for the second proofing.
- Baking: Preheat the oven and transfer the proofed dough to the baking vessel. Bake the bread at the specified temperature and time, allowing it to develop a golden crust and bake through.
You can confidently embark on your baking adventures by understanding the baking methods and techniques for cake and bread. So, whether you’re craving a fluffy cake or a chewy loaf of bread, follow these guidelines to create delicious baked goods that will impress everyone.
Remember, baking is both a science and an art, so don’t be afraid to experiment and adapt recipes to suit your taste. Happy baking!
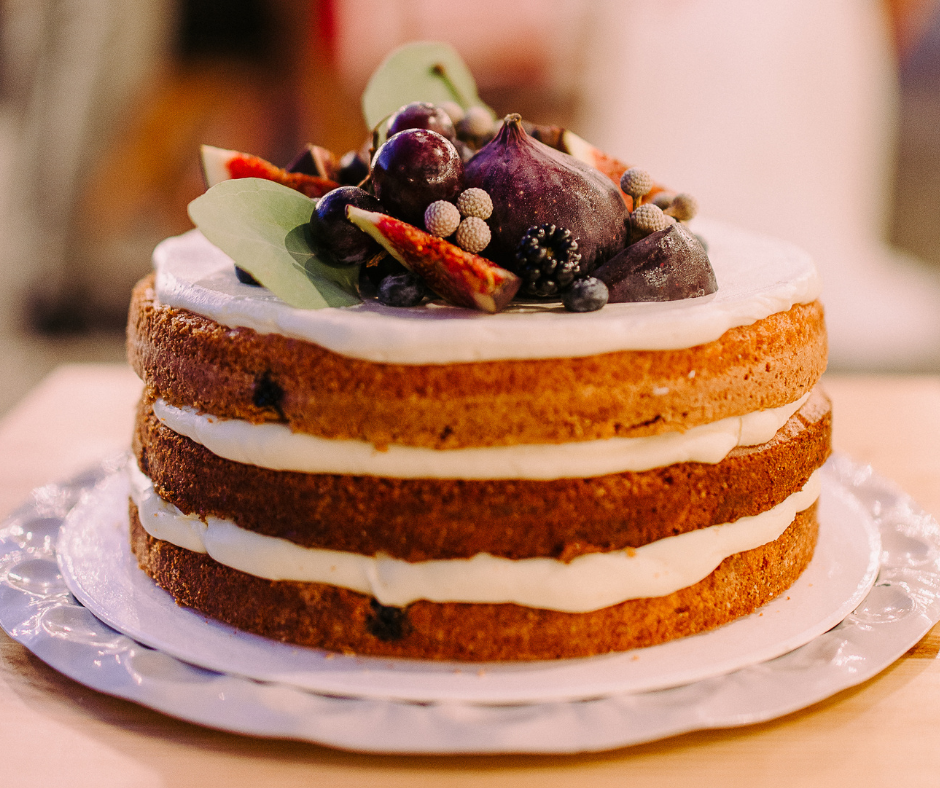

Sweet Breads And Loaf Cakes
Definition And Characteristics
Understanding the difference between sweet bread and loaf cakes is essential for achieving the desired results. While both fall under the baked goods category, they have distinct characteristics.
As the name suggests, sweetbreads are bread-like treats often sweetened and flavored with fruits, nuts, or spices. They are typically baked in a loaf pan and have a dense and moist texture. The main ingredients in sweet breads include flour, sugar, eggs, and butter or oil. Yeast is not typically used in sweet bread recipes, as they rely on chemical leaveners such as baking powder or baking soda.
Loaf cakes, on the other hand, are cakes that are baked in a loaf pan. They have a lighter and fluffier texture compared to sweet breads. The main ingredients in loaf cakes are similar to traditional cakes – flour, sugar, eggs, butter, or oil – but they often include additional flavorings such as cocoa powder, vanilla extract, or citrus zest. They are leavened with baking powder or soda, giving them a softer and more tender crumb.
Examples And Variations
There are countless variations of sweet bread and loaf cakes, each offering unique flavors and textures. Here are a few examples:
- Banana Bread: One of the most popular sweet breads, banana bread is moist and rich in flavor, thanks to the ripe bananas used in the recipe. It is often enhanced with nuts or chocolate chips.
- Lemon Poppy Seed Loaf Cake: This loaf cake is light and refreshing, with a tangy lemon flavor complemented by the crunch of poppy seeds. It can be served plain or with a glaze for added sweetness.
- Zucchini Bread: Combining the sweetness of bread with the moistness of zucchini, this loaf cake is a perfect balance of flavors. It is a great way to use up excess zucchini from your garden.
- Carrot Cake Loaf: Carrot cake in loaf form offers the same delicious flavors as the traditional layer cake, with the added convenience of a single pan. It is usually topped with a cream cheese frosting.
The endless possibilities for sweet bread and loaf cakes allow bakers to experiment with different flavors and ingredients to create unique treats that cater to their taste preferences.
By understanding the characteristics and variations of sweet bread and loaf cakes, home bakers can confidently embark on baking adventures and create delightful treats that will leave everyone wanting more. So, whether it’s a loaf of delicious banana bread or a fluffy lemon poppy seed cake, embrace the art of baking and let your creativity shine in the kitchen. Happy baking!
Conclusion
Understanding the Difference Between Cake and Bread is essential for any aspiring home baker. While both fall under the baked goods category, they have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Cakes are typically lighter and fluffier, with a tender crumb, while breads are denser and chewier, with a more substantial texture. The leavening agents used in each also differ, with cakes relying on baking powder or baking soda and bread using yeast for fermentation.
Summary Of The Differences Between Cake And Bread
To recap, here are the key differences between cake and bread:
- Texture: Cakes are lighter and fluffier, whereas breads are denser and chewier.
- Leavening Agents: Cakes are leavened with baking powder or baking soda, while breads rely on yeast for fermentation.
- Ingredients: Both cakes and breads share common ingredients such as flour, sugar, eggs, and fat (butter or oil). However, cakes often include additional flavorings and ingredients such as cocoa powder, vanilla extract, or fruits, while bread may incorporate nuts, grains, or seeds.
- Baking Method: Cakes are typically baked in round or square cake pans, while breads are baked in loaf pans or shaped into various forms.
- Purpose: Cakes are primarily served as a dessert or sweet treat, while bread can serve as a staple for sandwiches or accompaniments.
It’s important to note that while the term “quick bread” is sometimes used to describe a type of bread, it is a term that applies to dough or batter leavened with baking powder or baking soda rather than yeast.
Home bakers can confidently embark on their culinary adventures by understanding these basic baking principles. Whether it’s whipping up a light and airy cake for a celebration or kneading dough for a hearty loaf of bread, baking offers endless possibilities for creativity in the kitchen.
FAQ: Difference Between Cake and Bread: Understanding the Baking Basics
Q: What is the main difference between cake and bread?
A: The main difference between cake and bread is the leavening agents used. Bread is typically leavened with yeast, while cake is made using baking powder or baking soda. Additionally, including other ingredients such as sugar, eggs, milk, and fat can also affect the texture and taste of each.
Q: Are all breads leavened with yeast?
A: Yes, traditional breads are typically leavened with yeast. This includes various types of bread, such as white, wheat, and rye bread.
Q: How does cake differ from bread regarding texture and taste?
A: Cakes are known for their lighter and fluffier texture than bread, which tends to be denser. Cakes are almost always sweet and are often frosted or decorated. In contrast, bread is more savory and can vary in taste depending on the type of bread.
Q: Can bread and cake be made using the same baking methods?
A: Both bread and cake involve baking but utilize different leavening agents. Bread requires time for the yeast to activate and rise, while cake relies on chemical leavening agents like baking powder or baking soda for a quicker rise. The different methods result in distinctive textures and flavors.
Q: Can some cakes be baked in loaf pans and called bread?
A: Some cakes with a tight crumb can be baked in loaf pans and called bread. Examples include banana bread or pumpkin bread. Although they may resemble bread in shape, they are still considered cakes due to their sweetness and use of baking powder or baking soda as leavening agents.
Q: What about muffins and cupcakes? Are they similar to cake or bread?
A: Muffins and cupcakes fall into the same category as cakes. They are made using similar ingredients and leavening agents, with variations in size and presentation. However, “bread” is not typically associated with muffins or cupcakes.
Q: Are there any other significant differences between cake and bread?
A: Apart from the leavening agents used, cakes often incorporate additional ingredients such as flavorings, oils, or fats to enhance taste and texture. On the other hand, bread usually follows a simpler recipe with fewer added flavorings.
Q: Is it possible for cakes and breads to overlap in terms of texture and taste?
A: Yes, variations in cake and bread recipes can blur the line between the two. Some cakes may have a denser texture, similar to bread, while some breads may have added sweetness or flavors reminiscent of cake. However, the fundamental differences in leavening agents and ingredients differentiate the two categories.
Graham Bartlett, owner at Taco and Piña Mexican food, is all about bringing the authentic flavors of Mexico to your plate. With Graham Bartlett, you can tantalize your taste buds with mouthwatering tacos and delicious piña coladas, all in one place. Stay connected and never miss a beat as Graham Bartlett takes you on a culinary journey through vibrant Mexican cuisine. Join the community and discover the perfect blend of flavor, culture, and passion that Graham Bartlett brings to the table. Experience the essence of Mexico, one bite at a time, with Graham Bartlett.
